+86-13516964051
+86-13516964051 Methods for Optimizing Machining Allowances in Aluminum Alloy Castings
Methods for Optimizing Machining Allowances in Aluminum Alloy Castings
I. Why is Machining Allowance Optimization a Core Competitive Advantage in the Supply Chain?
As a global purchaser of aluminum alloy castings, are you facing these pain points:
* Cost waste due to excessive allowances amidst raw material price fluctuations (raw materials account for over 60% of each casting)
* Dimensional returns due to insufficient allowances in cross-border deliveries (industry average return rate reaches 3%-5%)
* Quality fluctuations caused by inconsistent allowance standards when collaborating with suppliers in multiple regions
* Machining allowances are not simply "material reserves," but a key lever for balancing procurement costs, production efficiency, and product precision. Data from an automotive parts supplier shows that after scientifically optimizing allowances:
* Raw material loss decreased by 12%-18% (based on a monthly purchase volume of 5000 units, annual cost savings exceed $100,000)
* Processing cycle shortened by 30% (adapting to flexible delivery needs for small batches and multiple deliveries)
* Scrap rate decreased from 8%-10% to below 3.5% (compliant with IATF 16949 automotive industry standard)

II. Three Core Optimization Methods
1. Dynamic Tolerance Allocation Method: Precise Calculation Avoids "Over-processing"
* The most practical allowance calculation formula in international procurement:
* Machining Allowance = Maximum Material Size - Design Size + Process System Error Compensation
* (Process system errors include variables such as machine tool vibration, tool wear, and thermal deformation)
* Specific parameters for low-Pressure Casting of aluminum alloys:
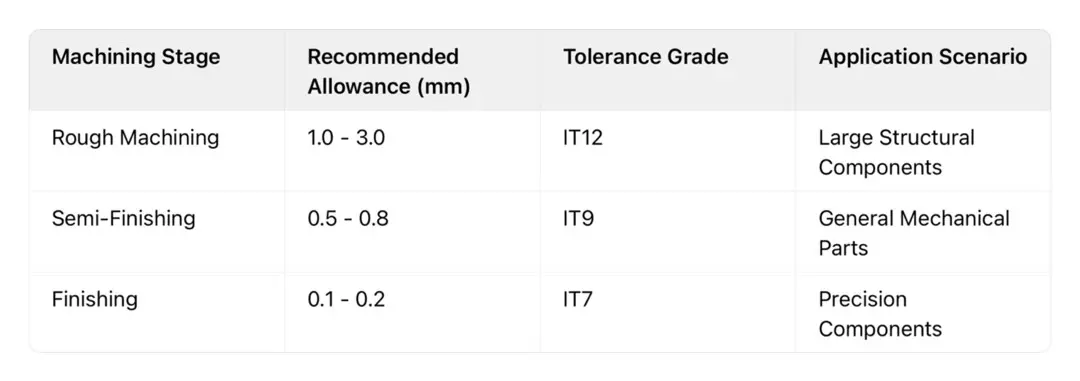
Key Technique: Introducing a dynamic adjustment coefficient K = 1.2 × Machine Tool Accuracy Coefficient + 0.8 × The material deformation coefficient can be flexibly adjusted according to the supplier's equipment level to avoid waste or risks caused by uniform standards.
2. End-to-End Collaborative Optimization: Closed-Loop Control from Design to Inspection
Design Phase: Suppliers are required to adopt "equal wall thickness transition" design (wall thickness difference ≤ 2mm), adding process ribs (width 1-1.5 times wall thickness), which can reduce initial deformation by 40%.
Casting Process: Metal mold/graphite mold casting is preferred (allowance can be reduced to 0.5-4mm), replacing traditional sand casting (allowance 3-6mm). CAE simulation reports (such as AnyCasting simulation of the filling process) are also required.
Inspection Standards: Clearly require compliance with ISO 8062 dimensional tolerances and ISO 28927 defect classification standards. Critical dimensions are inspected using coordinate measuring machines (accuracy ±0.02mm).
3. Intelligent Tool Application: Data-Driven Allowance Management
Suppliers can be required to configure the following during procurement:
Digital Twin System: Real-time monitoring of 200+ parameters such as injection force and mold temperature, with allowance deviation warning accuracy up to ±0.5%.
AI Predictive Model: Analyzes historical data using machine learning to automatically optimize the allowance allocation for different batches of castings.
Online Inspection Equipment: Prevents errors throughout the entire process from first piece to last piece, achieving a defective product interception rate of ≥99%.
III. Purchaser Implementation Guidelines: From Standard Agreements to Supplier Management
1. Core Contract Terms
* Clear Allowance Standards: Refer to GB/T 13819 (China) or ASTM B179 (USA), specifying "allowance 0.5-1mm for casting thickness ≤10mm; allowance 1-2mm for thickness >10mm."
* Quality Claims: Dimensional deviations ≤±0.05mm are considered acceptable; suppliers bear round-trip logistics costs for returns exceeding these limits.
* Data Delivery: Requires CAE simulation reports and allowance inspection records (including Ra surface roughness data) for each batch.
2. Key Supplier Evaluation Indicators
* Equipment Level: Whether the supplier possesses a servo die-casting machine (repeatability ±0.5%) and 3D-printed conformal cooling molds.
* Process Capabilities: Whether the supplier can achieve… "Three-stage injection molding + gradient holding pressure" process (low-pressure casting pressure 0.05-0.1MPa)
Case verification: Requires providing case studies of similar product margin optimization (including cost savings and efficiency improvement data).
3. Risk mitigation solutions
Small-batch trial production: Reserve 20% of the first order for trial production to verify the feasibility of the margin solution.
Multi-regional adaptation: Adopt the ISO 16220 chemical composition standard for suppliers in different regions to avoid margin adjustments due to material differences.
Emergency mechanism: Establish a rapid response process for abnormal margins (provide a rectification plan within 48 hours).

IV. Successful cases from international buyers
A new energy vehicle buyer optimized the margin of aluminum alloy motor housings through the following measures:
Required suppliers to adopt a ring gate design + conformal cooling channels, reducing the single-piece margin by 0.3mm.
Introduced SMED quick mold change technology, reducing mold change time from 4 hours to 90 minutes. Minutes Establish a dynamic margin database and fine-tune parameters based on the composition of different batches of aluminum alloy.
Ultimately achieve:
8% increase in raw material utilization (annual aluminum cost savings of $120,000)
45% reduction in delivery cycle (meeting the JIT supply requirements of overseas OEMs)
Unified margin standards across 5 global suppliers, reducing the quality complaint rate to 0.